Đề cương cứng ôn thi học tập kì 1 môn tiếng Anh lớp 9 bao gồm đáp án được Vn
Doc.com sưu tầm và đăng tải, là tài liệu xem thêm hữu ích dành riêng cho chúng ta học sinh lớp 9, giúp các bạn ôn tập cùng củng cố kỹ năng và kiến thức Từ vựng - Ngữ pháp học tập kì 1 lớp 9 môn giờ đồng hồ Anh công tác mới. Sau đây mời chúng ta vào tham khảo.
Bạn đang xem: Ôn tập tiếng anh lớp 9
I. Ngữ pháp giờ đồng hồ Anh học tập kì 1 lớp 9 đầy đủ
* Xem chi tiết tại: Ngữ pháp tiếng Anh lớp 9 học kì 1 năm 2022 - 2023
CHƯƠNG 1: CÁC THÌ vào TIẾNG ANH
1. THÌ HIỆN TẠI HOÀN THÀNH.* form: (+) S + has/ have + V- ed (pp) + O
(-) S + has/ have + not + V- ed (pp) + O
(?) Has/ have + S + V- ed (pp) + O?
PP = Past Participle quá khứ phân từ luật lệ V-ed: BQT coi cột 3 (V3)
* Adv: just, recently, ever, never, already, since, for, so far, yet, up to now, lately, twice, three times, many times, not...yet
eg: I have just seen my sister in the park. Note: (just,ever, never, already) đi sau have/has
She has finished her homework recently. (recently,lately,yet) đặt cuối câu.
* bí quyết dùng:
Diễn tả một hành vi vừa mới xảy ra.Hành động xảy ra trong vượt khứ nhưng không rõ thời gian.Hành động xẩy ra trong thừa khứ với còn liên quan đến bây giờ còn tiếp nối đến tương lai.Hành động xẩy ra lặp đi tái diễn nhiều lần.2. THÌ QUÁ KHỨ ĐƠNa. Với đụng từ Tobe:
* I/ He/ She/ It (Nam) Was * eg: nam was absent from class yesterday
* You/ We/ They (Nam and Lan) Were (Were Minh and Mai in hospital last month?
b. Với cồn từ thường:
* form: (+) S + V- ed/ (V2 BQT) + O *eg: Tom went lớn Paris last summer.
Câu bao phủ định và nghi ngờ ta buộc phải mượn trợ cồn từ did
(-) S + did not + Vinf + O (He did not watch TV last night.)
(?) Did + S + Vinf + O? (Did you go to sài gòn city two days ago?)
Adv: Yesterday, ago, last (week/ month/ year/ ...)
c. Phương pháp dùng thì thừa khứ đơn:
Diễn tả một hành động đã xẩy ra trong vượt khứ và dứt hẳn vào QK
3. THÌ QUÁ KHỨ TIẾP DIỄN* khung (+) S + Was/ were + V- ing + O
(-) S + Was/ were + not + V- ing + O
(?) Was/ were + S + V- ing + O?
Cách cần sử dụng thì quá khứ tiếp diễn:
Diễn tả một hành động đang xảy ra trong quá khứ tại 1 thời điểm khẳng định cụ thể.
=> I was doing my homework at 6 p.m last Sunday.
Diễn tả hai tốt nhiều hành vi cùng xảy ra trong thừa khứ. (While)
=> I was cooking while my sister was washing the dishes.
Diễn tả một hành vi xảy ra thì một hành vi khác đến cắt ngang.(When)
=> When the teacher came, we were singing a song.
CHƯƠNG 2: CÂU ĐIỀU KIỆN
I. định hướng về câu điều kiện Tiếng Anh.
Một câu điều kiện thường gồm hai mệnh đề là mệnh đề bao gồm và mệnh đề phụ (If). Mệnh đề phụ (If) hoàn toàn có thể đặt trước hoặc sau mệnh đề chính.
1. Câu đk 1: điều kiện rất có thể xảy ra.
* form:
| MỆNH ĐỀ IF | MỆNH ĐỀ CHÍNH |
| Simple present (HTđ) | Simple future (TLđ) |
| If + S + V(HT) + O, | S + Will/ Shall + V(inf) + O |
John usually walks to school if he has enough time.
If she eats much, she will be overweight.
2. Câu đk 2: điều kiện không có thật ở hiện nay tại.
* form:
| MỆNH ĐỀ IF | MỆNH ĐỀ CHÍNH |
| Past simple (QKĐ), | would/could/ should/ might + Vinf |
| If + S + V–ed (V2) + O, | S + would/ could + V(inf) + O |
* Note: Tobe cần sử dụng Were cho toàn bộ các ngôi (trong Mệnh đề If)
* eg: If I had much money, I would buy a new bicycle.
If I were you, I would not tell him about that.
3. Note: Unless = if...not (nếu không, trừ khi)
Eg: Unless it rains, we will go khổng lồ the movies. = (If it does not rain, we will go lớn the movies)
CHƯƠNG 3. CÁCH DÙNG ĐỘNG TỪ "WISH"
I. Lý thuyết.
Động từ bỏ Wish = If only (ao ước) hay sử dụng để biểu đạt những ước muốn, những điều không có thật hoặc rất khó thực hiện.
Có 2 nhiều loại câu ước.
1. Future wish: (ước mong ở tương lai)
* form: S1 + wish + S2 + would/ could + V(inf) + O.
If only + S + would/ could + V(inf) + O
* eg: I wish I would be an astronaut in the future.
Tom wishes he could visit Paris next summer.
If only I would take the trip with you next Sunday.
2. Present wish (ước muốn ở hiện nay tại)
* form: S1 + wish + S2 + V- ed + O
Were + adj / n * Note: Tobe sử dụng Were cho tất cả các ngôi
* eg: I wish I were rich (but I am poor now)
I can"t swim. I wish I could swim.
CHƯƠNG 4: CÂU BỊ ĐỘNG (THE PASSIVE VOICE)
Lý thuyết.
· quan sát:
- Câu chủ động: Mr Smith teaches English. (Active)
- Câu bị động: English is taught by Mr Smith. (Passive)
· Qui tắc:
- Tân ngữ chủ động ( công ty ngữ bị động
- Động từ bị động Be + Past Participle (pp)
- nhà ngữ dữ thế chủ động ( tân ngữ bị động (trước tất cả giới từ bỏ by chỉ tác nhân)
* Note: by them/ by people/ by someone …. Bỏ
Bảng nắm tắt công thức những thì trong câu bị động.
HTĐ | Am, is, are + V- ed (pp) |
QKĐ | Was, were + V- ed (pp) |
HTTD | Am,is, are + being + V- ed (pp) |
QKĐD | Was, were + being + V- ed (pp) |
HTHT | Have, has + been + V- ed (pp) |
MODEL VERBS | Can,may,might,should,will Have to, used to, + be + V- ed (pp) |
(Còn tiếp)
II. Bài xích tập ôn tập giờ đồng hồ Anh 9 học tập kì 1 có đáp án
I. SUPPLY THE CORRECT VERB FORM
1. Be quiet ! The baby (sleep) ...........................
2. It (not rain)..................... In the dry season.
3. His uncle (teach)................. English in our school five years ago.
4. They (not speak)....................... Khổng lồ each other since they quarreled
5. If Tom (go)......................to bed earlier, he would not be so tired.
6. If he (try)..................... Hard, he"ll pass the examination.
7. I wish someone (give) .................. Me a job next month.
8. The form teacher has asked Jack (write)...................... An essay on the Thames.
9. I advised him (wait)............................... For me at the airport.
10. Homework must (do).......................... Regularly.
Đáp án
1. Is sleeping | 2. Doesn’t rain | 3. Taught | 4. Haven’t spoken | 5. Went |
6. Tries | 7. Would give | 8. To write | 9. Khổng lồ wait | 10. Do |
II. TURN INTO PASSIVE FORM:
1. The chief engineer was instructing all the workers of the plant. ..........................................
2. Somebody has taken some of my books away. ..................................................................
3. They will hold the meeting before May Day. .......................................................................
4. They have to lớn repair the engine of the car.............................................................................
5. The boys broke the window and took away some pictures...................................................
Đáp án:
1. All the workers of the plan were being instructed by the chief engineer
2. Some of my book have been taken away
3. The meeting will be held before May Day
4. The engine of the oto has to lớn be repaired
5. The window was broken và some pictures were taken away by the shops
III. Bởi vì AS DIRECTED
1. Johnny said to lớn his mother, "I don"t know how to vì chưng this exercise."
Johnny told his mother ...................................................................................
2. "Don"t come back before one o"clock", advised my brother.
My brother advised me ..................................................................................
3. I often went fishing when I was young.
I used .............................................................................................................
4. My friend said, " Are you going lớn leave tomorrow?"
My friend asked me .......................................................................................
5. I asked Bill, "What time did you go to lớn bed last night?"
I asked Bill ....................................................................................................
6. It"s a pity. I can"t help her with her business
I wish .............................................................................................................
7. "We are waiting for the school bus", said the children.
The children said that ...................................................................................
8. "Listen to me và don"t make a noise,"said the teacher lớn his students.
The teacher asked his students ...................................................................
9. Because my sister studied hard, she completed her exam successfully (Rewrite,using " so")
My sister .......................................................................................................
10. "Let"s go for a walk." said Tam.
Tam suggested ............................................................................................
Đáp án:
1. Johnny told his mother he didn"t how to vì that exercise.
2. My brother advised me not to lớn come back before one o" clock.
3. My father used lớn go fishing when he was young.
4. My friend asked me I was going lớn leave the day after
5. I asked Bill what time he had gone lớn the bed the night before
6. I wish I could help her with her business
7. The children said that they were waiting for the school bus
8. The teacher asked his students to lớn listen lớn him and not to lớn make a noise
9. My sister studied hard, so she completed her exam successfully
10. Tam suggested going for a walk
IV. PHONETICS
From each number, pick out the word whose underlined part is pronounced differently from the others.
1. A. Out B. Round C. About D. Would
2. A. Chair B. Kiểm tra C. Machine D. Child
3. A. Too B. Soon C. Good D. Food
4. A. Though B. Enough C. Cough D. Rough
5. A. Happy B. Hour C. High D. Hotel
6. A. Equal B. Fashion C. Champagne D. Match
7. A. Only B. Cốt tông C. Cross D. Economic
8. A. Baggy B. Minority C. Style D. Symbol
9. A. Design B. Ghost C. Clothing D. Strong
10. A. Casual B. Sale C. Sleeveless D. Slit
Đáp án
1. D | 2. C | 3. C | 4. A | 5. B |
6. A | 7. A | 8. C | 9. B | 10. A |
V. MULTIPLE CHOICE: Choose the best answer to lớn complete the following sentences
1. I"ve played the piano ______.
A. Two years ago B. Since 1995 C. Before 1995 D. Tomorrow
2. He ______ me about it last night.
A. Tells B. Have told C. Has told D. Told
3. The meeting will ______ in London next week.
A. Be held B. Is held C. Be hold D. Are hold
4. Bananas ______ khổng lồ Europe every year.
A. Are exported B. Exports C. Is exported D. Exported
5. She wishes she ______ a palace now.
A. Owns B. Owned C. Is owning D. Would own
6. My house ______ broken into last night.
A. Are B. Is C. Was D. Were
7. The details should ______ carefully.
A. Is checked B. Check C. Was checked D. Be checked
8. If Mary doesn"t improve in math, we_____have to find a tutor for her.
A. Will B. Can C. Should D. Would
9. The journey khổng lồ the village is very __________.
A. Interested B. Interesting C. Disinterested D. Interest
10. I don"t lượt thích using the mạng internet because it has some _____
A. Benefits B. Advantages C. Limitations D. Disadvantages
Đáp án:
1. B | 2. D | 3. C | 4. A | 5. D |
6. C | 7. D | 8. A | 9. B | 10. D |
ERROR
Choose the underlined words or phrases that are not correct in standard written English.
1. Minh & I(A) haven’t seen (B) each other (C) for 2012 now (D) .
2. Don’t expect to learn (A) all words in a day (B). Learning language is (C) time-consumed (D) work.
3. Millions of people(A) have visit (B) Disney World in (C) Orlando, Florida, since (D) it opened.
4. This (A) is the first (B) time I tried (C) lớn play (D) badminton.
5. The last time (A) we decorated the flat was (B) 5 years ago. The flat wasn’t (C) decorated for (D) five years.
Đáp án
1 - D; 2 - D; 3 - B; 4 - C; 5 - C;
GAP FILLING
Read the passage và fill in each blank with a suitable word from the box.
working doing sound scientific adults writers universities angry computers have |
Today, computer companies sell many different programs for computers. First, there are programs for (1)_________ math problems. Second, there are programs for (2)_________ studies. Third, some programs are lượt thích fancy typewriters. They are often used by (3)_________ and business people. Other programs are made for courses in schools and (4)_________. & finally, there are programs for fun. They include word games and puzzles for children & (5)_________.
There are many wonderful new computer programs, but there are other reasons to like (6)_________. Some people lượt thích the way computers hum và sing when they are (7)_________. It is a happy sound, lượt thích the sounds of toys and childhood. Computers also (8)_________ lights & pretty pictures. And computers even seem to lớn have personalities. That may (9)_________ strange, but computers seem to lớn have feelings. Sometimes they seem happy, sometimes they seem (10)_________. It is easy khổng lồ think they are lượt thích people.
Đáp án
1 - doing; 2 - scientific; 3 - writers; 4 - universities; 5 - adults;
6 - computers; 7 - working; 8 - have; 9 - sound; 10 - angry;
Fill in each gap with ONE suitable word in the box:
convenient wear know impressed bởi vì different don’t |
1. I wish I had more time khổng lồ get to …………………… your beautiful country better.
2. My little daughter was really ………………. By the wonderful flowers in Da
Lat.
3. The design & material used lớn make the Ao dai for men were ………… from those used for women.
4. People lượt thích wearing jeans because it did not………………. Out easily.
5. Mạng internet is really wonderful. It’s very fast and………………. Way to lớn get information.
6. You love playing chess with your father in your miễn phí time,………………you?
Đáp án
1 - know; 2 - impressed; 3 - different;
4 - wear; 5 - convenient; 6 - don"t;
Read the following passage và choose the best answers.
Tet is a national and.................... (1) festival in Vietnam. It is occasion for every Vietnamese lớn be reunited khổng lồ think.................(2) their past activities & hope for good luck in the new year.
Before Tet all houses.................. (3) whitewashed and ...................... (4) with colourful lights. Everybody is looking......................... (5) khổng lồ a better life. In the new year’s eve, children are smartly dressed.......................... (6) are hoping to lớn receive money put in small red envelopes as they are wishing longevity to................... (7) grandparents & parents. Wrong doings should...................... (8) avoided on these days.
1. A. Traditional B. Modern C. Compulsory D. Convenient
2. A. About B. With C. After D. For
3. A. Was B. Were C. Are D. Is
4. A. Decorate B. Decorating C. Khổng lồ decorate D. Decorated
5. A. For B. Forward C. After D. At
6. A. Them B. Who C. These D. They
7. A. His B. Her C. My D. Their
8. A. Take B. Not C. We D. Be
Đáp án
1 - A; 2 - A; 3 - C; 4 - D;
5 - B; 6 - B; 7 - D; 8 - D;
Choose A, B, C or D khổng lồ complete the following passage:
English is a very useful language. If we (1)________ English, we can go to lớn any countries we like. We will not find it hard to make people understand (2)_________ we want to say. English also help us to learn all kinds of(3)__________ hundreds of books are (4)________in English everyday in (5)__________ countries. English has also helped lớn spread ideas and knowledge (6)__________ all corners of the world. Therefore, the English language has helped to lớn spread better (7)__________ và (8)_________ among the countries of the world.
1. A. To know B. Know C. Knew D. Known
2. A. What B. Where C. When D. How
3. A. Subjects B. Things C. Ideas D. Plans
4. A. Write B. Wrote C. Written D. Writing
5. A. Much B. Lot of C. Many D. A lots of
6. A. In B. With C. At D. To
7. A. To understand B. Understanding C. Understand D. Understood
8. A. Friend B. Friendly C. Friendliness D. Friendship
Đáp án
1 - B; 2 - A; 3 - A; 4 - C;
5 - C; 6 - D; 7 - B; 8 - D;
VIII. READING
1. Read the passage, and choose the correct answer A, B, C or D for each question.
The Complex of Hue Monuments is a UNESCO World Heritage Site và is located in the đô thị of Hue in central Vietnam. Hue was founded as the Viet phái nam capital city by Gia Long, the first king of the Nguyen Dynasty in 1802. It held this position for thirteen Nguyen kings until 1945.
The massive complex features hundreds of monuments & mins, such as the Forbidden Purple City, once the residence of the royal family và badly damaged during the Vietnam War. The Imperial City, royal tombs, the flag tower, pagodas, temples, a library và museum.
Hue, located on the banks of the Huong River, (also known as the Perfume River) is about a hundred kilometres north of da Nang. Among the most impressive monuments in this former grand imperial capital are the Ngo mon Gate of the Imperial city which once was exclusively used by the royal family và their servants & soldiers, the tomb of Emperor Minh sở hữu as well as the tomb of Emperor Tu Du
C. In fact, many of the monuments surrounding the royal buildings were constructed in the early 19th century and were modeled after Beijing’s Forbidden City. The wall that surroundings the citadel is six metres high và two và a half kilometres long.
The historical complex is known not only for its rich architecture but also for its beautiful landscape setting. Overall, the site is quite spectacular. Avoid Hue between October and December as it gets most of its rain from the northeast monsoon during that period. This small đô thị is also famous for its Imperial-style cuisine.
1. The Hue Citadel needs the work of restoration because of ___________.
A. The period from 1802 lớn 1945 B. The damage during the war
C. The northeast monsoon D. Its rich architecture
2. All of the following are mentioned as features of the Hue Citadel EXCEPT _________.
Đề cương ôn tập định hướng học kì 2 môn tiếng Anh 9 bắt đầu tổng hợp tổng thể kiến thức bám sát đít SGK và chương trình Tiếng Anh của bộ Giáo dục, giúp học viên hiểu và nắm rõ kiến thức sẽ học.
A. Topics:
1. Recipes and Eating Habits
2. Tourism
3. English in the World
4. Space Travel
5. Challenging Roles in Society
6. My Future Career
B. Intonation:
1. Tones in statements used as questions.
2. Tones in finding out questions
3. Tones in making sure questions
4. Tones in “known” và new information
5. Tones in listing things
6. High tones và flat voice in adjectives
C. Grammar:
I. CONDITIONAL SENTENCES (CÂU ĐIỀU KIỆN)
TYPE | IF CLAUSE | MAIN CLAUSE | USAGE |
TYPE 1 – Present Real Condition
| Simple Present S + Vo/ Vs/es | Simple Future S + WILL + Vo CAN MAY | Diễn tả điều kiện rất có thể xảy ra ở lúc này hoặc tương lai |
TYPE 2 – Present Unreal Condition
| Past Subjunctive S + V2/Ved (BE à WERE)
| Future in the past S + WOULD + Vo COULD MIGHT | Diễn tả điều kiện không thể xảy ra ở hiện tại tại |
Ví dụ:
- Type 1:
+ If it rains this evening, I won’t go out. (Nếu tối nay trời mưa tôi sẽ không ra ngoài.)
+ Lan will miss the bus if she doesn’t hurry. (Lan sẽ bỏ lỡ xe buýt giả dụ cô ấy ko khẩn trương lên.)
- Type 2:
+ If I were you, I would buy that book. (Nếu tôi là bạn, tôi sẽ tải quyển sách đó.)
+ He could buy a bike if he had enough money. (Anh ấy hoàn toàn có thể mua xe đạp điện nếu anh ấy bao gồm đủ tiền.)
- Unless (Trừ phi) = If …not (Nếu……. Không)
Ví dụ: If you don’t get up early, you will miss the bus. (Nếu các bạn không tỉnh dậy sớm các bạn sẽ bỏ lỡ xe buýt.)
= Unless you get up early, you will miss the bus.
II. CONNECTIVES (TỪ NỐI)
1. And, but, or:
a. And (và): là từ nối được dùng để làm nối các từ, các từ tốt mệnh đề với nhau.
Eg: + We buy vegetables, bread, fish and meat every day.
+ Yesterday she watered the flowers and went shopping.
+ James said that he was never late for class and that he always did his homework.
b. But (nhưng): để diễn tả một ý trái ngược cùng với ý nói trước đó.
Eg: + He is intelligent but lazy.
+ I lượt thích bananas but my brother doesn’t.
+ She tried hard but failed.
c. or (hoặc là/hay là): dùng đưa ra một sự lựa chọn.
Eg: + vì you come from France or German ?
+ Is that good or bad ?
2. So, because:
a. so (vì vậy/ vì chưng thế).
Eg: She heard the bad news, so she cried.
b. because (bởi vì/ do).
Eg: She cried because she heard the bad news.
3. However, therefore:
a. However (tuy nhiên): được sử dụng để diễn tả một ý trái ngược với ý nói trước đó.
Eg: She rich and beautiful. However, she is not happy.
b. Therefore (do đó/vì thế): đựơc dùng để làm chỉ hậu quả.
Eg: He’s busy. Therefore, he can’t help you.
III. ARTICLES (MẠO TỪ)
"a" cùng "an" cần sử dụng chỉ hầu hết sự vật, hiện tại tượng ví dụ người nghe ko biết, "The" chỉ sự việc toàn bộ cơ thể nói và người nghe hầu như biết.
1. Mạo từ bỏ “the”
- sử dụng “the” khi nói đến một trang bị riêng hoặc một fan mà khắp cơ thể nghe và fan nói phần nhiều biết.
Ví dụ: The dog is on the chair. (Con chó ở trên ghế ấy.)
- “the” cũng khá được dùng để nói về một đồ vật thể hoặc vị trí đặc biệt, duy nhất.
Ví dụ: The Eiffel Tower is in Paris. (Tháp Eiffel sinh sống Paris.)The Earth revolves around the Sun. (Trái Đất xoay bao quanh mặt trời.)
- Trong một số trong những trường hợp, “the” rất có thể dùng cùng với danh từ bỏ số ít và số nhiều.
Ví dụ: the cát (con mèo), the cats (những nhỏ mèo)
- “the” đứng trước danh từ, xác định bằng một nhiều từ hoặc một mệnh đề.
Ví dụ: The girl in uniform is my sister. (Cô gái mang đồng phục là chị của tôi.)
- Mạo từ bỏ “the” đứng trước từ bỏ chỉ sản phẩm công nghệ tự của vụ việc như "first" (thứ nhất), "second" (thứ nhì), "only" (duy nhất)
Ví dụ: The first day (ngày đầu tiên)The best time (thời gian tiện lợi nhất) The only way (cách duy nhất)
- "the" + danh từ bỏ số ít bảo hộ cho một tổ động vật, một loại hoặc đồ vật vật
Ví dụ: The whale is in danger of becoming extinct. (Cá voi đã có nguy hại tuyệt chủng.)
- "the" sử dụng với 1 thành viên của một tổ người tuyệt nhất định
Ví dụ: The small shopkeeper is finding business increasingly difficult. (Giới nhà tiệm nhỏ dại nhận thấy việc bán buôn ngày càng nặng nề khăn.)
- Mạo từ "the" đứng trước tính trường đoản cú chỉ một đội nhóm người, một tầng phần bên trong xã hội
Ví dụ: the old (người già), the rich & the poor (người giàu và người nghèo)
- cần sử dụng trước số đông danh từ riêng biệt chỉ biển, sông, quần đảo, dãy núi, tên thường gọi số nhiều của những nước, sa mạc, miền
Ví dụ: The Pacific (Thái Bình Dương), The Netherlands (Hà Lan)
- "the" + tên chúng ta (dạng số nhiều) chỉ gia tộc...
Ví dụ: The Smiths (Gia đình đơn vị Smiths)
2. Mạo tự “a” và “an”
- “A” với “An” gồm cách sử dụng gần giống nhau. Mặc dù nhiên, dùng “An” lúc chữ đằng sau bước đầu bằng nguyên âm (a, o, u e,i) và cần sử dụng “A” khi chữ đằng sau bước đầu bằng các phụ âm còn lại.
Ví dụ: An hour (một giờ), a dog (một nhỏ chó)
- tự “A” và “An” sử dụng khi danh từ người nói nhắc đến không quánh biệt.
Ví dụ: I would lượt thích an apple. (Tôi hy vọng một trái táo.)
- “A” cùng “An” dùng để làm giới thiệu về máy lần thứ nhất nhắc tới với người nghe (người nghe chưa chắc chắn gì về sản phẩm này). Sau thời điểm giới thiệu, người nói rất có thể dùng mạo từ bỏ “The” khi nhắc tới vật đó.
Ví dụ: John has a dog & cat. The dog is called Rover, & the cat is called Fluffy. (John tất cả một con chó cùng một con mèo. Chú chó tên là Rover với chú mèo thương hiệu là Fluffy.)
- Trong một vài trường hợp, “A”, “An” được dùng với danh trường đoản cú số ít
Ví dụ: A cát (một bé mèo)
3. Không áp dụng mạo từ
- Mạo từ ko được sử dụng khi nói về việc việc tầm thường hoặc nhắc đến ví dụ.
Ví dụ: I don’t lượt thích apples. (Tôi không thích táo.)
- một vài tên quốc gia, thành phố, những bang không cần sử dụng mạo tự đứng trước.
Ví dụ: I live in London. (Tôi sống trong London.)
Trừ trường hòa hợp của The Philippines, The United Kingdom, The United States of America.
- Tên các môn học không thực hiện mạo từ
Ví dụ: John studies economics & science.
- Trước tên quốc gia, châu lục, núi, hồ, đường.
Ví dụ: Europe (châu Âu), South America (Nam Mỹ), France (Pháp)
- Sau tính từ thiết lập hoặc sau danh trường đoản cú ở thiết lập cách
Ví dụ: The girl"s mother (Mẹ của cô ấy gái)
- Trước tên gọi các bữa ăn.
Ví dụ: They invited some friends to lớn dinner. (Họ mời vài ba người bạn đến nạp năng lượng tối)
- Trước những tước hiệu
Ví dụ: King Louis XIV of France (Vua Louis XIV của Pháp)
- Trong một trong những trường hợp sệt biệt
Ví dụ: In spring/in autumn (vào mùa xuân/mùa thu), last night (đêm qua), next year (năm tới), from beginning to kết thúc (từ đầu cho tới cuối), from left to lớn right (từ trái quý phái phải).
IV. RELATIVE CLAUSES (MỆNH ĐỀ quan tiền HỆ)
Mệnh đề quan hệ nam nữ là mệnh đề bắt đầu bởi các đại từ quan hệ như who/whom/which/whose/that và các trạng từ quan hệ giới tính như where/when. Bao gồm hai các loại mệnh đề quan liêu hệ: Mệnh đề quan lại hệ xác định (defining) với không xác minh (non-defining).
1. Mệnh đề quan hệ tình dục xác định.
Là mệnh đề quan trọng phải tất cả để làm công dụng giới hạn, làm rõ nghĩa danh trường đoản cú đứng trước nó. Mệnh đề này thường không tồn tại dấu phẩy trước cùng sau nó.
Eg: I don’t know the girl whom/that you met yesterday.
2. Mệnh đề quan hệ tình dục không xác định.
Là mệnh đề không cần thiết phải bao gồm để làm công dụng giới hạn danh trường đoản cú đứng trước nó, nghĩa là bản thân danh từ đứng trước nó bổ nghĩa. Chính vì như vậy mệnh đề này thường dùng sau danh từ riêng rẽ hoặc các danh từ xẻ nghĩa ( Mr. Pike, Mrs. Hoa, ..), thường sẽ có dấu phẩy trước cùng sau nó.
Eg: Mr. Pike , who is my neighbor , is very nice.
3. Relative pronouns (Đại từ quan liêu hệ)
Functions ( Chức năng) | Defining (Xác định) | Non-defining (Không xác định) | |
Subject ( nhà ngữ ) | Người | WHO / THAT | WHO |
Vật | WHICH / THAT | WHICH | |
Object ( Tân ngữ ) | Người | WHOM / THAT | WHOM |
Vật | WHICH / THAT | WHICH | |
Posessive ( tải ) | Người | WHOSE | WHOSE |
Vật | WHOSE | WHOSE |
4. Relative adverbs.
- When => time
Ví dụ: Monday is the day. We will come then.
=> Monday is the day when we will come.
- Where => place
Ví dụ: I never forget the village. I was born there.
=> I never forget the village where I was born.
V. THE PAST SIMPLE TENSE (THÌ QUÁ KHỨ ĐƠN)
1. Form
TO BE:
(+): S + was/ were
(-): S + was/were not (=wasn’t/weren’t)
(?): Was/Were + S +…?
ĐỘNG TỪ THƯỜNG:
(+): S + V-ed/ cột 2 bảng đụng từ bất quy tắc
(-): S + did not (didn’t) + V(inf)
(?): Did + S + V(inf)
Notes: Qui tắc thêm ED:
- Động từ tận cùng bằng “e” câm. Thì chỉ việc thêm “d”: change => changed, love => loved.
- Động từ tận cùng bằng một phụ âm trước nó là nguyên âm duy nhất, trước lúc thêm “ed” phải gấp đôi phụ âm cuối: stop =>stopped, rub =>rubbed; hug => hugged.
- hồ hết động từ tận cùng bằng “y” trước nó là một trong những phụ âm thì thay đổi y =>i trước lúc thêm “ed”: try => tried
2. Use (Cách dùng)
Diễn tả một hđ đã xảy ra và hoàn thành ở một thời điểm xác minh trong quá khứ. Thường đi kèm với những từ chỉ thời gian: yesterday, ago, last/night, week, month…, in 1990…Ex: Yesterday he went trang chủ late.
Kể lại một chuỗi hành vi xảy ra liên tục.Ex: The man came to the door, unlocked it, entered the room, went to bed & lay down on it.
Một bài toán làm thường xảy ra, một kinh nghiệm trong quá khứ. Hay đi cùng với phó từ tần suất.Ex: I spoke Chinese when I was young.
VI. THE PAST PERFECT TENSE (THÌ QUÁ KHỨ HOÀN THÀNH)
1. Khái niệm:
Thì vượt khứ trả thành: dùng để miêu tả một hành vi xảy ra trước một hành động khác cùng cả hai hành động này rất nhiều đã xảy ra trong quá khứ. Hành vi nào xẩy ra trước thì cần sử dụng thì thừa khứ hoàn thành. Hành động xảy ra sau thì sử dụng thì vượt khứ đơn.
2. Cấu trúc:
Câu khẳng định | Câu bao phủ định | Câu nghi vấn |
S + had + Vp Ví dụ: – He had gone out when I came into the house. (Anh ấy vẫn đi ra bên ngoài khi tôi vào nhà.) – They had finished their work right before the deadline last week .(Họ đã hoàn thành các bước của bọn họ ngay trước hạn chót vào tuần trước.) | S + hadn’t + Vp – hadn’t = had not Ví dụ: – She hadn’t comehome when I got there. (Cô ấy vẫn không về bên khi tôi về.) – They hadn’t finishedtheir lunch when I saw them. (Họ vẫn không ăn xong bữa trưa khi trông thấy họ). | Had + S + Vp Trả lời: Yes, S + had. No, S + hadn’t. Ví dụ: – Had the film endedwhen you arrived at the cinema? (Bộ phim đã kết thúc khi các bạn tới rạp chiếu phim phim cần không?) Yes, it had./ No, it hadn’t |
VII. THE PASSIVE VOICE (CÂU BỊ ĐỘNG)
1. Phương pháp chuyển câu chủ động sang bị động
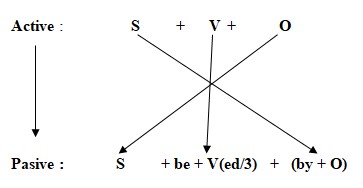
Ví dụ: Mr Manh teaches English.
=> English is taught by Mr Manh.
*Note : - ví như trong câu có khá nhiều trạng từ bỏ thị khi đưa sang câu thụ động chúng được bố trí theo lắp thêm tự sau :
Thể phương pháp + nơi chốn + thời gian
Trạng từ bỏ chỉ xứ sở được để trước By + O
Trạng tự chỉ thời gian được để sau By + O
- trường hợp câu dữ thế chủ động có 2 tân ngữ thì 1 trong 2 tân ngữ hoàn toàn có thể làm S vào câu bị động.
Ví dụ: He gave me a pen.
=> I was given a pen by him.
=> A pen was given to lớn me by him.
2. Some special Passive form:
a. Questions:
Ex: Who wrote that play? => By whom was that play written?
Have they read the letter? => Has the letter been read?
b. Material agent:
Ex: Smoke filled the room. => The room was filled with smoke.
c. Negative pronoun agent:
Ex: Nobody can unlock the case. -> The case can’t be unlocked.
d. Sentences with two objects:
Ex: Mary’s parents gave her a birthday present.
=> Mary was given a birthday present by her parents.
=> A birthday present was given to Mary by her parents.
3. Câu bị động của các thì:
Tenses | Active | Passive |
Hiện tại 1-1 giản | S + V_(s/es) | S + am/is/are + V_(ed/3) + by + O |
Quá khứ solo giản | S + V_(ed/2) | S + was/were + V_(ed/3) + by + O |
Hiện tại tiếp diễn | S + am/is/are + V-ing | S + am/is/are + being +V(ed/3) + by + O |
Quá khứ tiếp diễn | S + was/were + V-ing | S + was/were + being + V(ed/3) + by + O |
Hiện tại hoàn thành | S + have/has + V(ed/3) | S + have/has + been + V(ed/3) + by + O |
Tương lai đối chọi và hễ từ khuyết thiếu | S + will/can/... + V | S + will/ can…+ be + Ved/3 + by + O |
4. Một số trong những trường hợp bị động khác:
a. Bị động với “ have / get something done ”: bề ngoài bị rượu cồn này được thực hiện để nhấn mạnh vấn đề rằng hành động của đơn vị được thực hiện của fan khác.
Eg: Someone painted John’s flat yesterday.
=> John had his flat pạinted yesterday.
b. Tiêu cực với vẻ ngoài nguyên thể (infinitive) với danh hễ từ (gerund ).
Eg: + We dọn’t want lớn be refused entry.
+ She hates being photographed.
c. Thụ động với những động từ bỏ chỉ cách nhìn ( verbs of opinion ): believe, know, say, report, think,… bề ngoài bị cồn này thường được sử dụng khi fan nói ý muốn tránh nói tới nhà thể thực hiện hành động.
It + to be + PII(ed/cột 3) + that + clause.
Hoặc: S + khổng lồ be + PII(ed/cột 3) + to-inf/to have + PII(ed/cột 3).
VIII. ADVERB CLAUSES OF CONCESSION (MỆNH ĐỀ TRẠNG NGỮ CHỈ SỰ NHƯỢNG BỘ)
1. Although / even though / though + clause: khoác dù…
- We continued working although we were tired. = Although we were tired, we continued working.
- I didn’t get the job even though I had all the necessary qualifications. = Even though I had all the necessary qualifications, I didn’t get the job.
- I couldn’t sleep though I was very tired.
- Though the girl isn’t beautiful,I like her voice
- Even though I seee him every day,I’ve never spoken to lớn him.
2. In spite of / Despite + noun / noun phrase
- Although the traffic was bad, I arrived on time. = In spite of / Despite the bad traffic, I arrived on time.
Xem thêm: Công ty tnhh thương mại giải trí hải âu hosocongty, công ty giải trí hải âu tuyển dụng
- Although it rained heavily, we enjoyed our vacation. = We enjoyed our vacation in spite of / despite the heavy rain.